Lesson 8: Tenses
In this section, we will take an in-depth look at tenses and how they can affect what our sentences mean.
Objectives:
- To define tenses
- To discuss the importance of tenses and how they affect the meaning of our sentences
- To provide examples of how all the kinds of tenses are used in a sentence
- To enumerate when each tense is appropriate
Quick Navigation through the Lesson 8:
 Tenses refer to the way in which we state things, according to when they happened. There are three basic verb tenses in which we say things—past, present and future.
Tenses refer to the way in which we state things, according to when they happened. There are three basic verb tenses in which we say things—past, present and future.
Past tense refers to things that have already happened. We usually add –d or –ed to the end of a verb which has taken place in the past (walked, danced)—although there are some words to which this can’t be done. In these cases, we modify the words in a specific way (sit becomes sat or leave becomes left).
Present tense refers to things that are happening as we speak. We add –ing to verbs which denote present action (eat, eating). If the base verb ends with an e, it is usually omitted before adding the –ing (create, creating).
Future tense refers to things which we assume will take place in the future. We use words like will and shall to describe these actions (will be eating, will eat).
Throughout this lesson, we’ll discuss the different kinds of ways that these three basic tenses are manipulated to discuss the things we mean. We will also be taking a look at numerous examples which will help us understand how to use these tenses the right way and in the right instance.
[WpProQuiz 116]
Simple Tenses
This is (as the name suggests) the simplest of all the types of tenses. Here, past present and future are dictated by the basic verb tenses. This is used for simpler sentences when we simply mean that something has, is or will be happening.
Below are some examples of the simple tenses.
i. Simple Present Tense
The present tense utilizes the basic form of the verb to describe when the action is happening.
For example:
type or in a sentence, this would be: They type.
ii. Simple Past Tense
Here, we simply add –d or –ed to the base verb.
type + –d = typed or in a sentence: She typed.
iii. Simple Future Tense
In this case, we simply add the words will or shall to the base (simple present form) verb.
will + type = will type or in a sentence: She will type the paper later.
Now that we’ve discussed the simple tenses, it’s time to move onto the slightly more complex cases. We learn the difference in describing something that took place last week and something that took place the other day. We also learn how to stress when something is currently in progress.
[WpProQuiz 117]
Progressive Tenses
This tense stresses when something is, was or will be in progress at a certain time. Its basic form is the base verb + -ing—if the verb ends in a consonant, we double the last letter before adding the –ing.
For example:
run + (double the last letter) + -ing = running
And if it ends in an e, we omit the e before adding the –ing.
For example:
tune – e + -ing = tuning
This tense is the most active of all the tenses because it conveys immediate action. This can be used to convey actions that happen in the past, present and future.
Present Progressive Tense
This is used to denote something which is currently in progress. It simply makes use of the –ing form of the verb.
For example:
My niece is watching television.
Past Progressive Tense
This is used to denote something which was in progress at a certain period in time. It is often used in order to take the listener or reader back to the time when it happened as it portrays action more vividly than the simple past tense.
It uses was + the –ing form of the verb.
For example:
Six months ago, I was running a marathon that spanned over 50 kilometers.
Future Progressive Tense
This is usually used to describe an action which will be in progress in the future. Using the future progressive tense helps the listener imagine the action and the immediacy of it happening more vividly than the simple future tense.
It uses the form will be + the –ing permutation of the verb.
For example:
This time next year, I will be swimming in the hot springs with a drink in hand.
Perfect Tenses
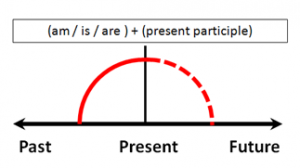 Perfect tense refers to an action which began in the past and continues either into the present or future. It utilizes the participle form of the verb, which is the non –ing permutation of the action.
Perfect tense refers to an action which began in the past and continues either into the present or future. It utilizes the participle form of the verb, which is the non –ing permutation of the action.
For instance, the word eaten is the participle form of eating.
In this part of this lesson, we will be discussing how this applies to the three basic verb tenses.
i. Present Perfect Tense
This utilizes the form has (for singular subjects)/have (for plural subjects) + the past participle form of the verb.
For example:
He has taken too many shots tonight.
They have mixed up their definitions.
ii. Past Perfect Tense
This utilizes the form had + the past participle form of the verb.
For example:
He had been a scholar all his life before the surgery.
They had been in love, as far as he was concerned.
iii. Future Perfect Tense
This utilizes the form will have + the past participle form of the verb.
For example:
If she wins the next championship, she will have won every contest ever held.
[WpProQuiz 118]
Perfect Progressive Tenses
The perfect progressive tenses are used to refer to actions which have occurred in the past but have recurred in the present or are expected to repeat themselves in the future.
i. Present Perfect Progressive Tense
This refers to an action which began in the past and finished in the past but which has some relevance to the present.
It utilizes the form has + been + the –ing form of the verb.
For example:
It has been raining for the past few days.
She has been crying for the last couple of nights.
ii. Past Perfect Progressive Tense
This refers to an action which took place in the past and was completed before another action which also took place in the past.
It utilizes the form had + been + the –ing form of the verb.
For example:
It had been sunny up until I got out of the car.
They had been friends before they met her.
iii. Future Perfect Progressive Tense
This indicates an action which began in the past and which will continue into the future.
It utilizes the form will + have+ been+ the –ing form of the verb.
For example:
By next Christmas, I will have been working for two years.
In this lesson, we learned about the different tenses and how to use them. We talked about the different ways in which we can apply the tenses to different situations and to the three basic verb tenses, depending on what we want to say and when it happened.
Next, we’ll be studying the different irregular verbs, how they’re used and how we can master them—we’ll be taking up the different patterns that they contain and will be looking at examples of how to use them in a sentence. Keep reading—we’re another step closer to having excellent English grammar.
 + 1-888-827-0150
+ 1-888-827-0150 + 44-20-3006-2750
+ 44-20-3006-2750